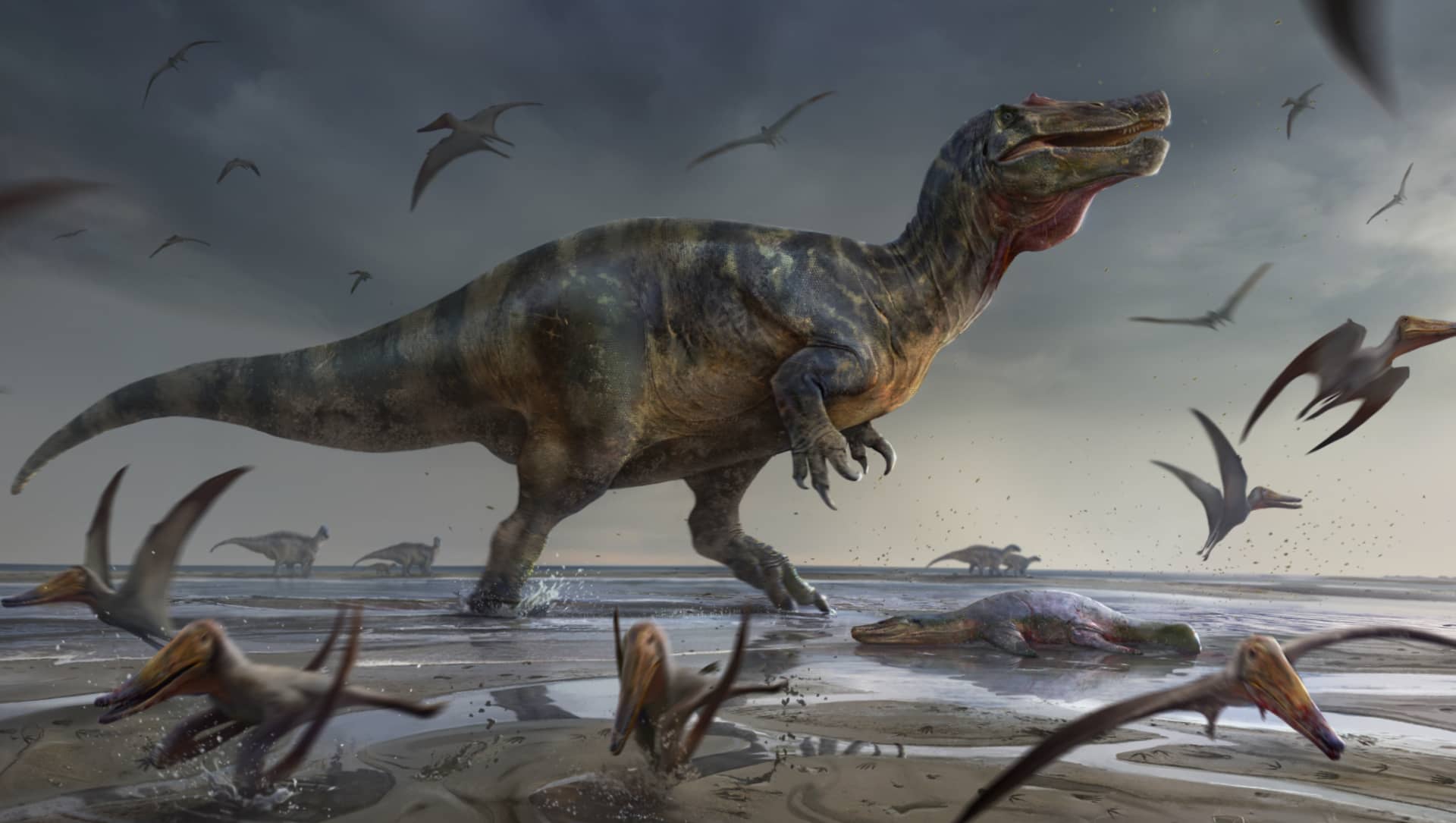
Research led by palaeontologists at the University of Southampton has identified the remains of one of Europe’s largest ever land-based hunters — a dinosaur that measured more than ten metres long and lived around 125 million years ago.
Several prehistoric bones, uncovered on the Isle of Wight, belonged to a type of two-legged, crocodile-faced predatory dinosaur known as spinosaurids.
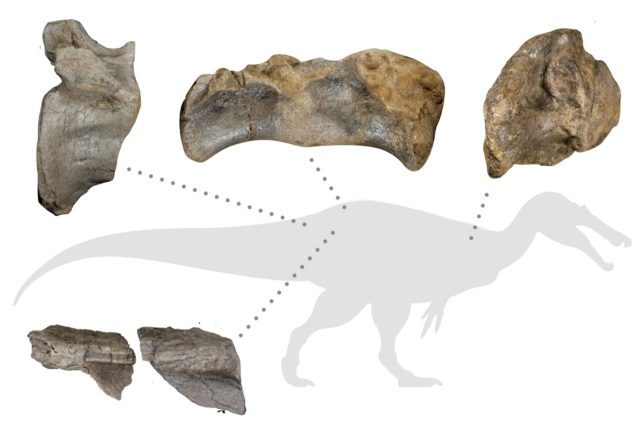
The ‘White Rock spinosaurid’
Dubbed the ‘White Rock spinosaurid’ – after the geological layer in which it was found – it was a predator of impressive proportions.
It is hoped the remains will go on public display at Dinosaur Isle, Sandown, in time for the school summer holidays.
Dr Martin Munt, the museum’s curator and general manager, said,
“Spinosaurs are amongst the most exciting and widely debated groups of dinosaurs; the museum has the remains of three different types which is unrivalled.”
Barker: May be largest predatory dinosaur found in Europe
PhD student Chris Barker, who led the study, said,
“This was a huge animal, exceeding ten metres in length and probably several tonnes in weight.
“Judging from some of the dimensions, it appears to represent one of the largest predatory dinosaur ever found in Europe – maybe even the biggest yet known.
“It’s a shame it’s only known from a small amount of material, but these are enough to show it was an immense creature.”
The discovery follows previous work on spinosaurids by the University of Southampton team, which published a study on the discovery of two new species in 2021.
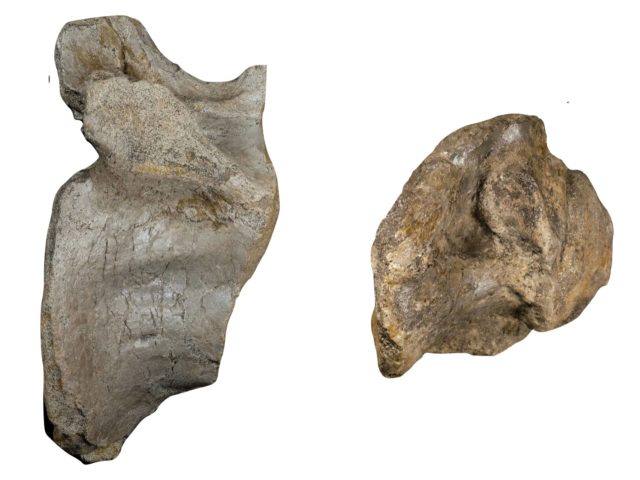
The bones of the ‘White Rock spinosaurid’, which include huge pelvic and tail vertebrae, among other pieces, were discovered near Compton Chine.

The Cretaceous rocks are famous for their dinosaurs, but little appreciated is the fact that the Island’s fossil record preserves dinosaurs from more than one section of history – and some of those sections, even today, are poorly known.
Gostling: Likely to be youngest spinosaur material yet known from the UK
Corresponding author Dr Neil Gostling, who teaches evolution and palaeobiology at the University of Southampton, said,
“Unusually, this specimen eroded out of the Vectis Formation, which is notoriously poor in dinosaur fossils.
“It’s likely to be the youngest spinosaur material yet known from the UK.”
Vectis Formation
The 125 million year old Vectis Formation preserves the beginning of a period of rising sea levels, where the ‘White Rock spinosaurid’ stalked lagoonal waters and sandflats in search of food.
Co-author Darren Naish said,
“Because it’s only known from fragments at the moment, we haven’t given it a formal scientific name.
“We hope that additional remains will turn up in time.
“This new animal bolsters our previous argument – published last year – that spinosaurid dinosaurs originated and diversified in western Europe before becoming more widespread.”
Marks on the bone also showed how, even after death, the body of this giant probably supported a range of scavengers and decomposers.
Lockwood: Most of the fossil were found by the late Nick Chase
Co-author Jeremy Lockwood, a PhD student at the University of Portsmouth and Natural History Museum, said,
“Most of these amazing fossils were found by Nick Chase, one of Britain’s most skilled dinosaur hunters, who sadly died just before the Covid epidemic.
“I was searching for remains of this dinosaur with Nick and found a lump of pelvis with tunnels bored into it, each about the size of my index finger. We think they were caused by bone eating larvae of a type of scavenging beetle. It’s an interesting thought that this giant killer wound up becoming a meal for a host of insects.”
The researchers hope to generate thin sections of the material to look at the microscopic internal properties of the bones in the near future, which may provide information about its growth rate and possible age.
The paper ‘A European giant: a large spinosaurid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Vectis Formation (Wealden Group, Early Cretaceous)’, UK is published in the journal PeerJ.
News shared by Isle of Wight council press office, in their own words. Ed
Image: © UoS Anthony Hutchings





